![]()
Ocean Freight
When it comes to exporting goods, there are a few different options available to business owners.
One of the most popular methods is ocean freight export, which can be an affordable and efficient way to move products around the world.
This comprehensive guide will tell you everything you need to know about this process – from how it works to what’s involved in shipping your goods overseas.
What is Ocean Freight Export?
Ocean cargo transport is responsible for nearly 90% of global commerce by capacity, solidifying its status as the titan of international shipping. In this method of transportation, substantial quantities of merchandise are securely stored in containers and conveyed by vessels worldwide.
This approach is the most effective and cost-friendly means of transporting vast amounts of goods. Additionally, ocean freight boasts a commendable safety history and is deemed more environmentally friendly compared to alternative shipping methods, such as air transport.
Ocean freight shipping is typically used for goods that are too heavy or bulky to be transported by air freight. This method is a great option for businesses and individuals who need to transport both large and small quantities of goods that are not time-sensitive.
Advantages of Exporting via Ocean Freight
There are many advantages to using ocean freight for your shipping needs. Some of these advantages include:
- Cost-effective: Shipping via ocean is generally less expensive than air freight, especially for large or heavy goods.
- Reliable: Shipping by sea is generally very reliable, with set schedules and fewer delays than air freight.
- Capacity: Shipping bulky or oversized freight is usually done by ocean containers as they can accommodate large volumes of cargo.
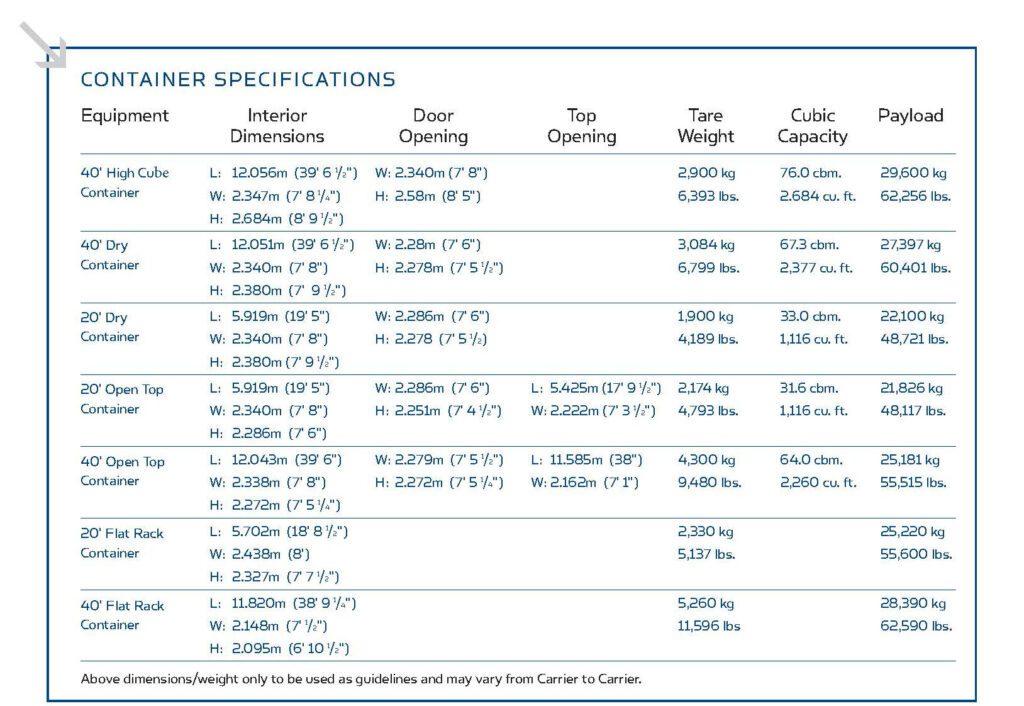
Standard Shipping Containers
*Note that the interior dimensions may vary slightly depending on the specific model and manufacturer of the container. Additionally, the number of pallets that can fit may also depend on the size and type of the pallets being used.
Standard containers used in ocean cargo transportation are typically constructed from steel and occasionally aluminum. They adhere to standardized dimensions as determined by the International Organization for Standardization. The most frequently utilized containers include the 20-foot, 40-foot, and 40-foot high-cube varieties.
Types of Ocean Freight Services
There are several types of ocean freight services available to suit different types of cargo and shipping needs. These include:
Full Container Load (FCL)
FCL shipping involves the use of a full container for your goods. This option is best for larger shipments that require a dedicated container. FCL shipping is generally faster and more secure than LCL shipping, as your goods are not co-mingled with other shipments.
Less than Container Load (LCL)
LCL shipping is used for smaller shipments that do not require a full container. Your goods will be consolidated with other shipments in the same container, which can be a more cost-effective option for smaller volumes of cargo.
Roll-on/Roll-off (Ro-Ro)
Ro-Ro shipping is used for vehicles or other rolling cargo that can be driven onto and off the ship. This option is generally faster and more cost-effective than other types of shipping for goods on wheels.
Export Documentation Requirements
When shipping goods by sea, several documents are required for customs clearance and other purposes. These documents include:
Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading is a legal contract between the shipper and carrier. It contains important details such as the shipper, consignee, and carrier names, a description of the goods, the origin and destination ports, and the terms of the shipment.
Commercial Invoice
The commercial invoice is a document that provides details about the goods being shipped, such as their value, quantity, and description. It is used for customs purposes and to determine the cost of duties and taxes that will be assessed.
Packing List
A packing list is a comprehensive record of all the goods being shipped, which includes vital details such as size, weight, and packaging for each item.
Certificate of Origin
The origin certificate is an authoritative document that furnishes critical details about the country where the goods in the shipment were produced. It is used for customs purposes and to determine whether the goods qualify for preferential treatment under a free trade agreement.
Other Documents
Along with the previously mentioned documents, the transportation of certain goods and the regulations of the receiving nation may call for additional paperwork to be submitted. These may include permits, licenses, or certificates.
Factors Affecting Ocean Freight Costs
Several factors can impact the cost of shipping goods by sea. These include:
Freight Rates
Freight rates are the charges levied by the carrier for transporting your goods. Rates can vary depending on the route, the type of cargo, and which carrier is handling the transportation.
Fuel Surcharges
Fuel surcharges are additional fees that are added to the freight rate to account for fluctuations in fuel prices.
Port Charges
Port charges are fees levied by the port authority for using the port facilities. They can include charges for handling, storage, and other services.
Customs Duties and Taxes
Customs duties and taxes are fees levied by the importing country on imported goods. The range of these charges may alter depending on the particular goods being delivered and the origin country.
Insurance
Insurance is an additional cost that may be required to protect your goods during transport. Insurance rates can differ for each shipment depending on the value of the goods being shipped and the level of coverage required.
Choosing a Partner
Choosing the right ocean freight export partner is crucial to ensuring that your goods arrive at their destination on time and in good condition. There are several types of partners to choose from, including:
Freight forwarders are companies that specialize in arranging the transportation of goods on behalf of their clients. They can handle all aspects of the shipping process, including documentation, customs clearance, and insurance.
Non-Vessel Operating Common Carriers (NVOCCs)
NVOCCs are companies that do not own their own ships but arrange for the transportation of goods on behalf of their clients. They typically have contracts with multiple carriers and can offer a range of shipping options.
Ocean Carriers
Ocean carriers are shipping companies that own and operate their own ships. They can offer a range of services, including FCL, LCL, and Ro-Ro shipping.
Preparing Your Goods for Export
Properly preparing your goods for ocean freight export is essential to ensuring that they arrive at their destination in good condition. Some things to consider when preparing your goods include:
Packaging and Labeling
Your goods should be properly packaged and labeled to protect them during transport and to facilitate customs clearance.
Customs Compliance
This is a critical step when importing and exporting goods. You must ensure that your goods comply with the customs requirements of the importing country. This may include obtaining permits, licenses, or certificates.
Hazardous Materials
If you are shipping hazardous materials, you will need to comply with the regulations governing the transportation of dangerous goods by sea.
Temperature Control
If your goods require temperature control, such as perishable goods or pharmaceuticals, you will need to request a quote specifically for temperature-controlled containers.
Tracking Your Ocean Freight Shipment
Tracking your ocean freight shipment is essential to ensuring that you know where your goods are always. Some things to consider when tracking your shipment include:
Tracking Tools
Most carriers offer online tools for tracking that allow you to monitor the status of your shipment often in real time! Make sure that the forwarder you work with offers this service.
Communication with Your Freight Forwarder
Your freight forwarder should be your first point of contact for regular updates on the status of your shipment. They should also be proactive in relaying any potential delays or other issues affecting your shipment.
Insurance Coverage
Protect your business by purchasing adequate insurance coverage for your goods in case of loss or damage during transport.
Customs Clearance and Import Duties
Clearing customs and paying import duties and taxes is a critical part of the ocean freight export process. Some things to consider when dealing with customs clearance and import duties include:
Customs Clearance Process
The customs clearance process can be complex and it is quite easy to make mistakes. Your freight forwarder can help you navigate this process and ensure that all required documentation is in order.
Import Duties and Taxes
Duties and taxes levied on imported goods may differ depending on the specific products and the country they come from. Your freight forwarder and a licensed Customs broker are invaluable resources to help you determine the cost of duties and taxes that will be assessed.
Free Trade Agreements
Free trade agreements can help to reduce or eliminate import duties and taxes for certain goods. Your freight forwarder can help you determine whether your goods qualify for preferential treatment under a free trade agreement.
Conclusion
Transporting goods by sea offers an economical and dependable method for international shipping, offering various options like full-container load (FCL) and less-than-container load (LCL). However, the process can be complex, especially for new shippers.
By familiarizing yourself with the different types of ocean freight services, required documentation (such as the Bill of Lading and Commercial Invoice), factors affecting shipping costs (like distance, weight, and dimensions), and proper preparation of goods (including packaging and labeling), you can ensure your cargo arrives at its destination in good condition and within the expected timeframe.
Or
Call us if you have questions or want to find out more about BGI
800-987-4244
FAQs
1: What is the difference between FCL and LCL shipping?
FCL shipping involves the use of a full container for your goods, while LCL shipping involves consolidating your goods with other shipments in the same container. FCL shipping is generally faster and more secure, while LCL shipping can be a more cost-effective option for smaller volumes of cargo.
2: How do I choose the right ocean freight export partner?
Choosing the right partner to help export your freight depends on a variety of factors, including your shipping needs, budget, and the reputation of the carrier. Always work with an experienced and reputable freight forwarder, this will help to ensure that your entire shipping process runs smoothly and efficiently.
3: What documents are required for freight export?
The documents required for ocean freight export include the Bill of Lading, commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and any additional documents required by the importing country.
4: What factors can affect the cost of shipping goods by sea?
Factors affecting the cost of shipping goods by sea include freight rates, fuel surcharges, port charges, customs duties and taxes, and insurance.
5: How can I ensure that my goods are properly prepared for export?
To ensure that your goods are properly prepared for ocean freight export, you should properly package and label your goods, ensure that they comply with customs requirements, comply with regulations governing the transportation of dangerous goods, and ensure that temperature-controlled goods are shipped in appropriate containers.