![]()
Staying competitive in the global Export marketplace
Introduction:
Expanding your business by exporting goods overseas can open new revenue streams and increase market reach.
The U.S. is one of the world’s largest exporters, supplying products to countries across the globe.
However, understanding what goods are in demand, where they are most commonly shipped, and how to navigate the complexities of international trade is crucial for success.
This guide will walk you through the most commonly exported goods from the U.S., their top destinations, and the key challenges businesses face when shipping internationally.
We’ll also provide strategies to overcome these challenges, ensuring your business remains competitive in the global marketplace.
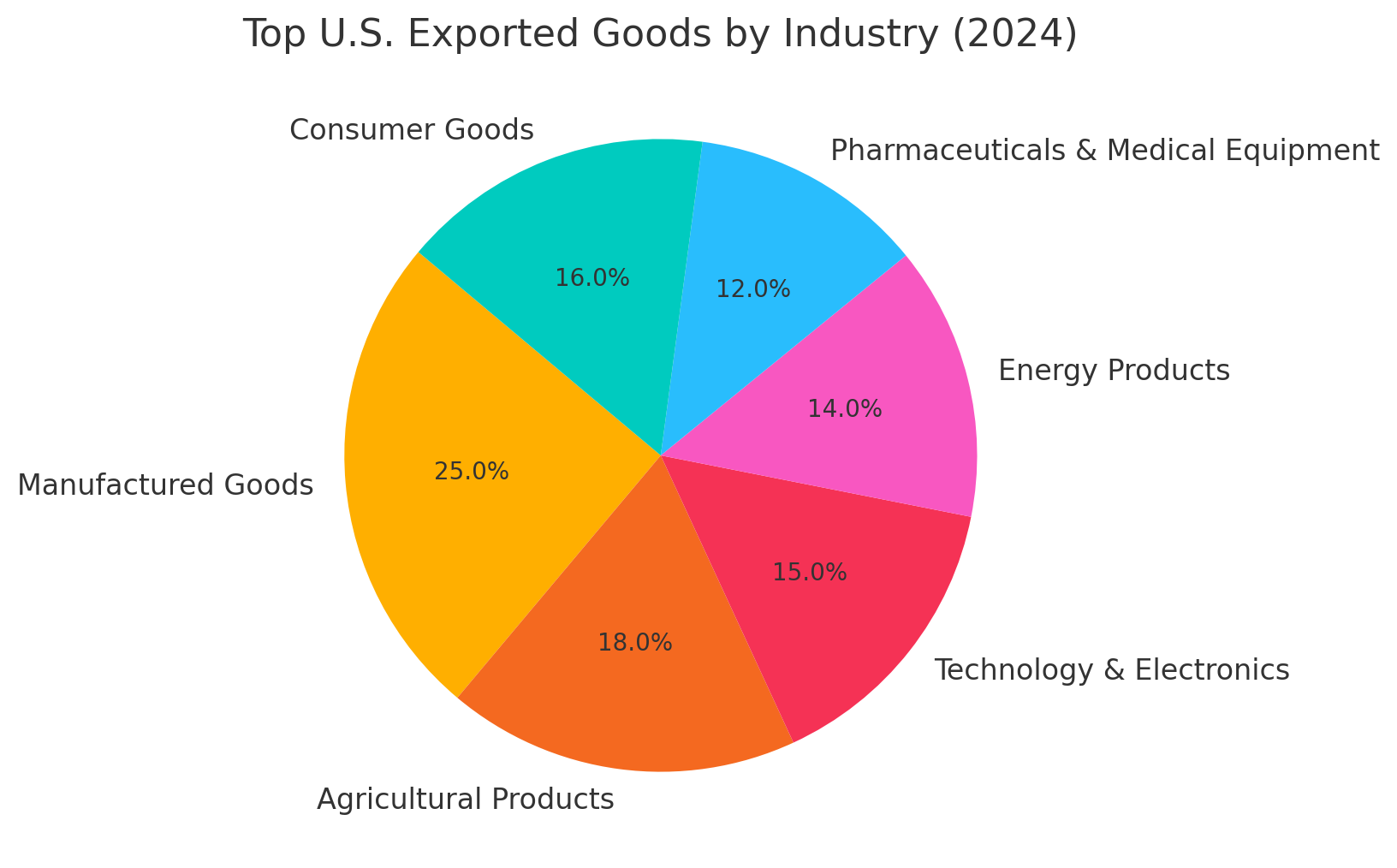
1. What Goods Does the U.S. Commonly Export?
The United States exports a wide range of goods, spanning multiple industries. Below is an overview of the top export categories:
Manufactured Goods
- Automobiles and auto parts
- Industrial machinery
- Electrical equipment and components
Agricultural Products
- Soybeans, corn, and wheat
- Dairy products and meat
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
Technology & Electronics
- Semiconductors and computer components
- Medical devices and healthcare technology
- Telecommunications equipment
Energy Products
- Crude oil and refined petroleum
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
- Coal
Pharmaceuticals & Medical Equipment
- Vaccines and prescription drugs
- Diagnostic tools and laboratory equipment
Consumer Goods
- Apparel and footwear
- Beauty and personal care products
- Packaged food and beverages
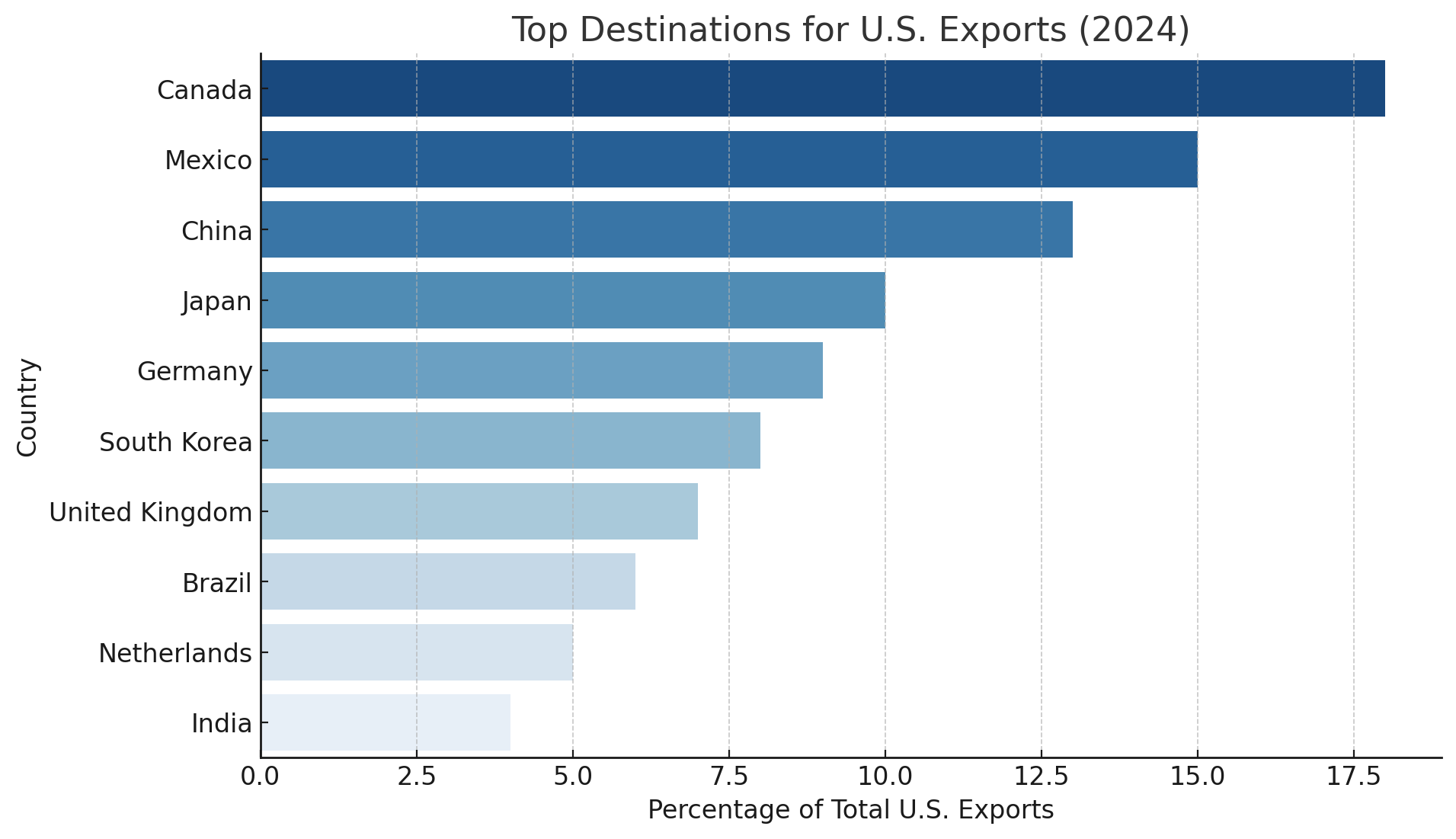
2. Top Destinations for U.S. Exports
The U.S. exports goods to almost every country, but specific markets consistently rank as top destinations:
| Country/Region | Major U.S. Exports |
|---|---|
| Canada | Automobiles, machinery, energy products |
| Mexico | Industrial equipment, agricultural products, electronics |
| China | Soybeans, semiconductors, medical devices |
| Japan | Pharmaceuticals, aircraft parts, food products |
| Germany | Chemicals, auto parts, aerospace components |
| South Korea | Medical equipment, energy products, technology |
| United Kingdom | Pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, software |
Source: U.S. Goods Trade with Global Partners
3. Common Challenges in Exporting Goods Overseas
While exporting can be highly profitable, businesses must navigate several challenges:
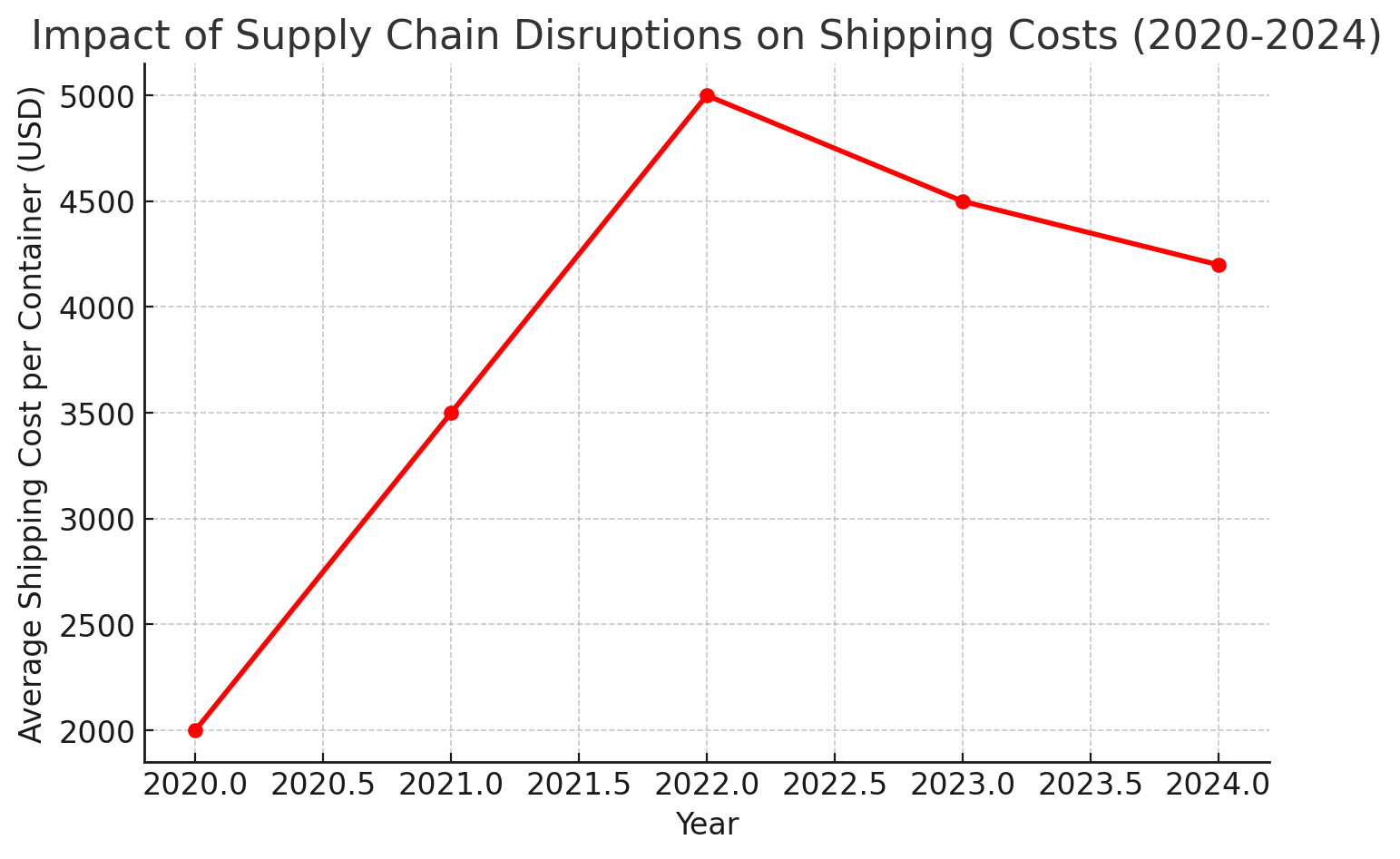
A. Supply Chain Disruptions
- Port congestion causes long wait times for shipments.
- Freight rate volatility, leading to increased costs.
- Container shortages, resulting in shipment delays.
- Geopolitical issues affecting trade relationships.
Source: Impact Of Supply Chain Disruptions On Shipping Costs (2020-2024)
B. Compliance & Regulatory Hurdles
Navigating export regulations can be complex. Some key considerations include:
- Export licenses and documentation: Ensure compliance with U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) regulations.
- Customs clearance: Incorrect paperwork can lead to shipment delays.
- Sanctions and trade restrictions: The U.S. restricts exports to certain countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea).
C. Currency Fluctuations & Payment Risks
- Exchange rate volatility can impact profit margins.
- International payment risks, including delays in receiving funds.
- Using secure payment methods like letters of credit can mitigate financial risks.
D. Logistics & Freight Forwarding Issues
- Choosing the right Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) is crucial for risk management.
- Air vs. ocean freight: Businesses must weigh the cost vs. speed.
- Last-mile delivery challenges can arise in international markets.
4. Strategies to Overcome Exporting Challenges
To successfully export goods overseas, businesses should implement the following strategies:
A. Optimizing the Supply Chain
- Diversify suppliers to minimize disruptions.
- Schedule shipments ahead of time to prepare for potential delays.
- Utilize freight tracking technologies for real-time visibility.
B. Compliance & Regulatory Hurdles
- Work with a licensed customs broker to navigate compliance requirements.
- Stay updated with changes in export control laws.
- Use an Export Management System (EMS) to keep documentation organized.
C. Managing International Transactions
- Implement hedging strategies to protect against currency fluctuations.
- Use trade credit insurance to safeguard against non-payment risks.
- Partner with reputable international banks for secure transactions.
D. Choosing the Right Freight Forwarding Partner
- Look for a freight-forwarding company with experience in your industry.
- Consider a third-party logistics (3PL) provider for global supply chain solutions.
- Evaluate their network coverage, reliability, and customer service.
5. Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Exporting goods overseas presents significant opportunities for U.S. businesses, but success requires careful planning.
Understanding which products are in demand, where to ship them, and how to navigate global challenges allows companies to expand their reach and increase profitability.
Key Takeaways:
✅ The U.S. exports manufactured goods, agricultural products, technology, and pharmaceuticals worldwide.
✅ Canada, Mexico, China, and Europe are the top destinations for U.S. exports.
✅ Supply chain disruptions, regulatory challenges, and currency risks can impact export operations.
✅ Planning shipments, ensuring compliance, and working with reliable freight forwarders are key to success.
BGI Worldwide Logistics offers premium freight-forwarding services to make exporting goods from the U.S. effortless and efficient.
Our comprehensive range of services caters to all shipping needs.
With cost-effective and hassle-free solutions, we guarantee that you will receive a professional and reliable shipping experience.
Choose BGI for all your freight needs and experience the difference with unmatched logistics expertise and customer care.
Call: 800-987-4244
Click below to get a quote
Explore our blog for more shipping tips and insights.